📄 2: Build Your Knowledge Base
Welcome to the second step of your Testus Patronus journey! In this exercise, you'll learn how to build a Knowledge Base that your AI assistant can search through using retrieval-augmented generation (RAG).
This is where your assistant starts to understand your testing documentation, requirements, and historical issues.

📌 What You'll Learn
🧠 Embeddings
When a document is ingested, it's transformed into a vector representation using an embedding model. These vectors help the AI understand meaning and similarity between pieces of text.
Embeddings let the model know that "bug report" and "defect ticket" might refer to the same concept.
In this tutorial, we use the model text-embedding-ada-002 from Azure OpenAI.
🍰 Chunking: Breaking Text into Pieces
📏 Chunk Size
Your documents are too long to fit directly into the model's input window, so they are divided into chunks.
| Chunk Size | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Small Chunks (200–300 tokens) | 🎯 High precision 🔍 Matches narrow queries well | 🧩 May lose broader context |
| Large Chunks (800–1000 tokens) | 📚 Preserve more context 🔁 Fewer retrievals needed | 🧊 More noise 🎯 Lower match precision |
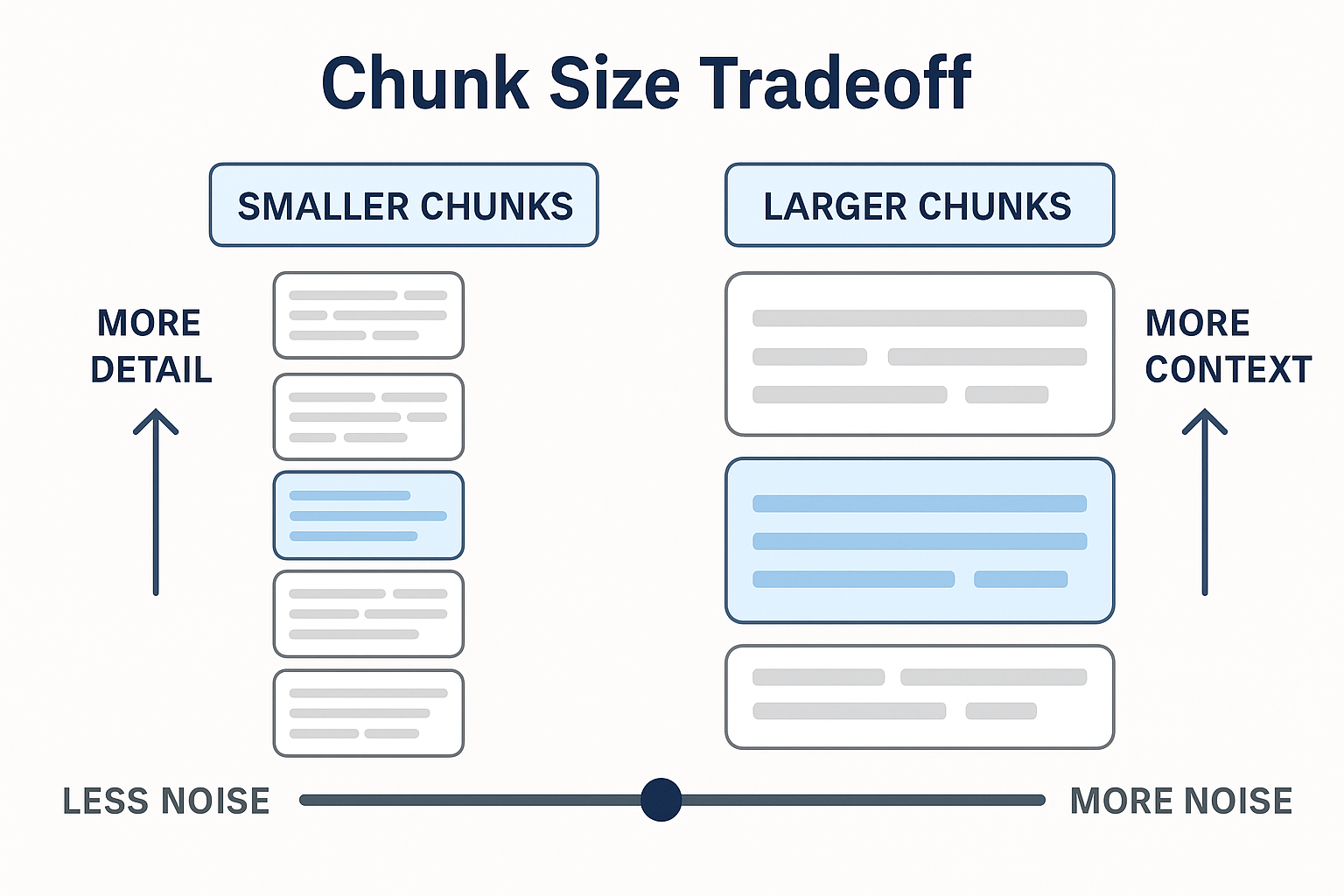
Think of it like reading pages of a book — too many pages at once and the meaning blurs. Too few and you lose the plot.
🔄 Chunk Overlap
Overlap ensures that context near the boundaries of chunks isn't lost.
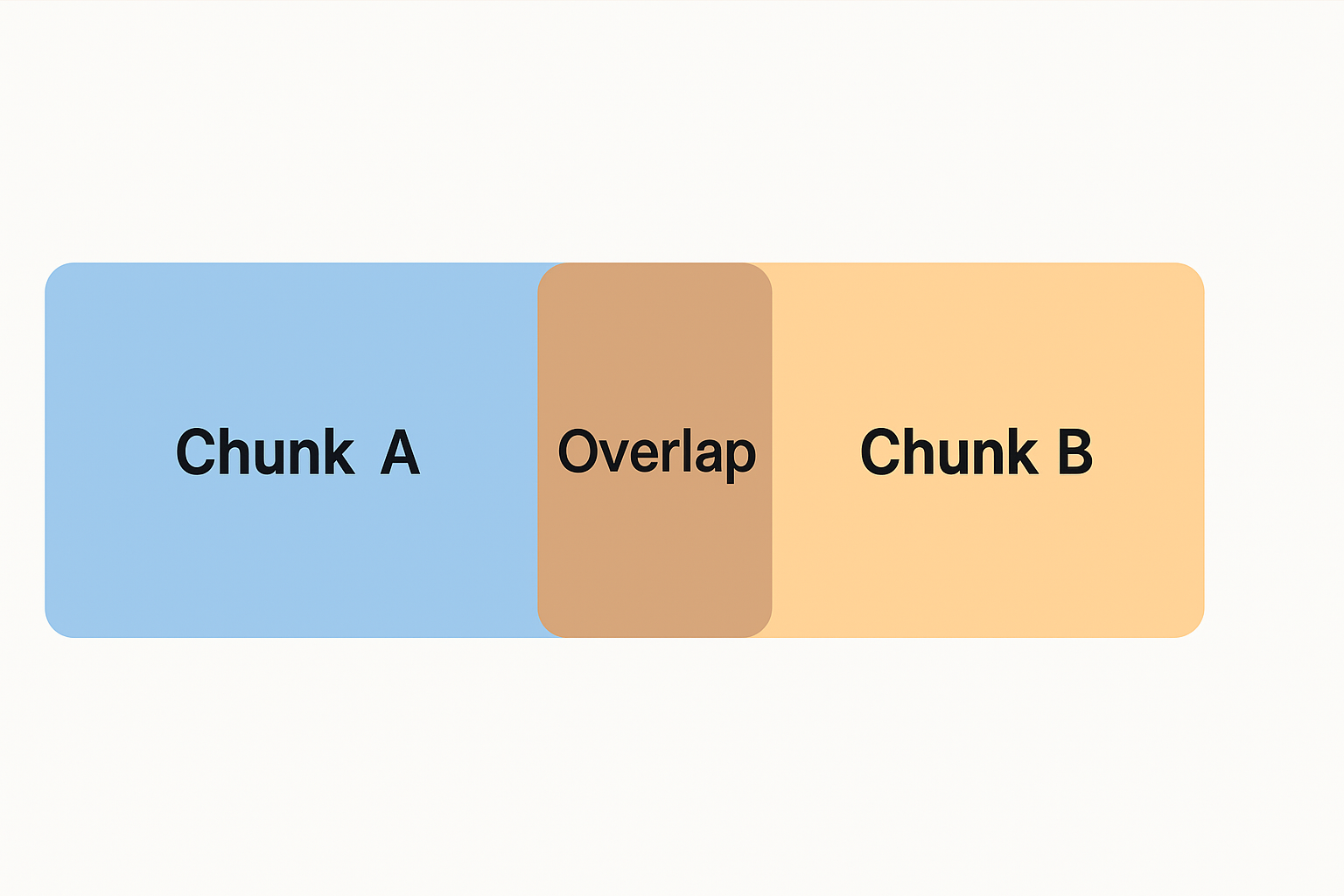
For example, if two chunks overlap by 100 tokens, the second chunk repeats the last 100 tokens of the first. This helps the model "remember" what came before — improving answers that need continuity.
🎯 Ranking and top-k Retrieval
Once you have all your documents chunked and embedded, you'll want to find the most relevant ones to a query.
This is where ranking comes in:
- The retriever uses cosine similarity (or a similar metric) to score each chunk.
- Then it picks the top K chunks (usually 3–5) with the highest scores.
- These are sent to the LLM for final answer generation.
top K right can dramatically improve performance!🛠️ Step-by-Step: Ingesting Documents
📝 Manual Upload via Dify UI
- Go to the Knowledge tab in your Dify instance.
- Click Create Knowledge.
⬇️ Download Jira Dataset Files
- Unzip the dataset and upload the files to the Knowledge Base.
- Upload
WEBHOOKS_JiraEcosystem_issues.txtandWEBHOOKS_JiraEcosystem_issues_SUMMARY.txtmanually. - Click on Next.
Configure:
- Chunk size: Start with 2000 characters.
- Overlap: Try 200 characters (10% of chunk size).
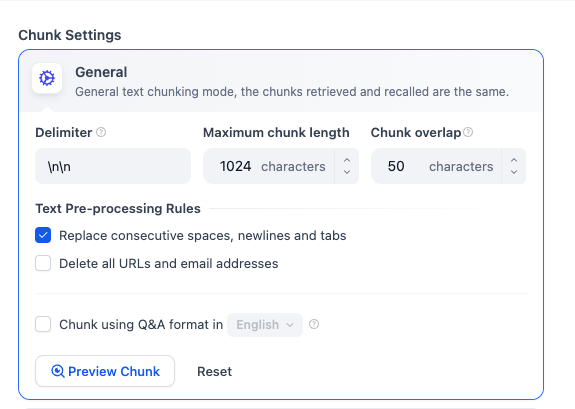
Select High Quality index method and select the text-embedding-3-large embeddings model.
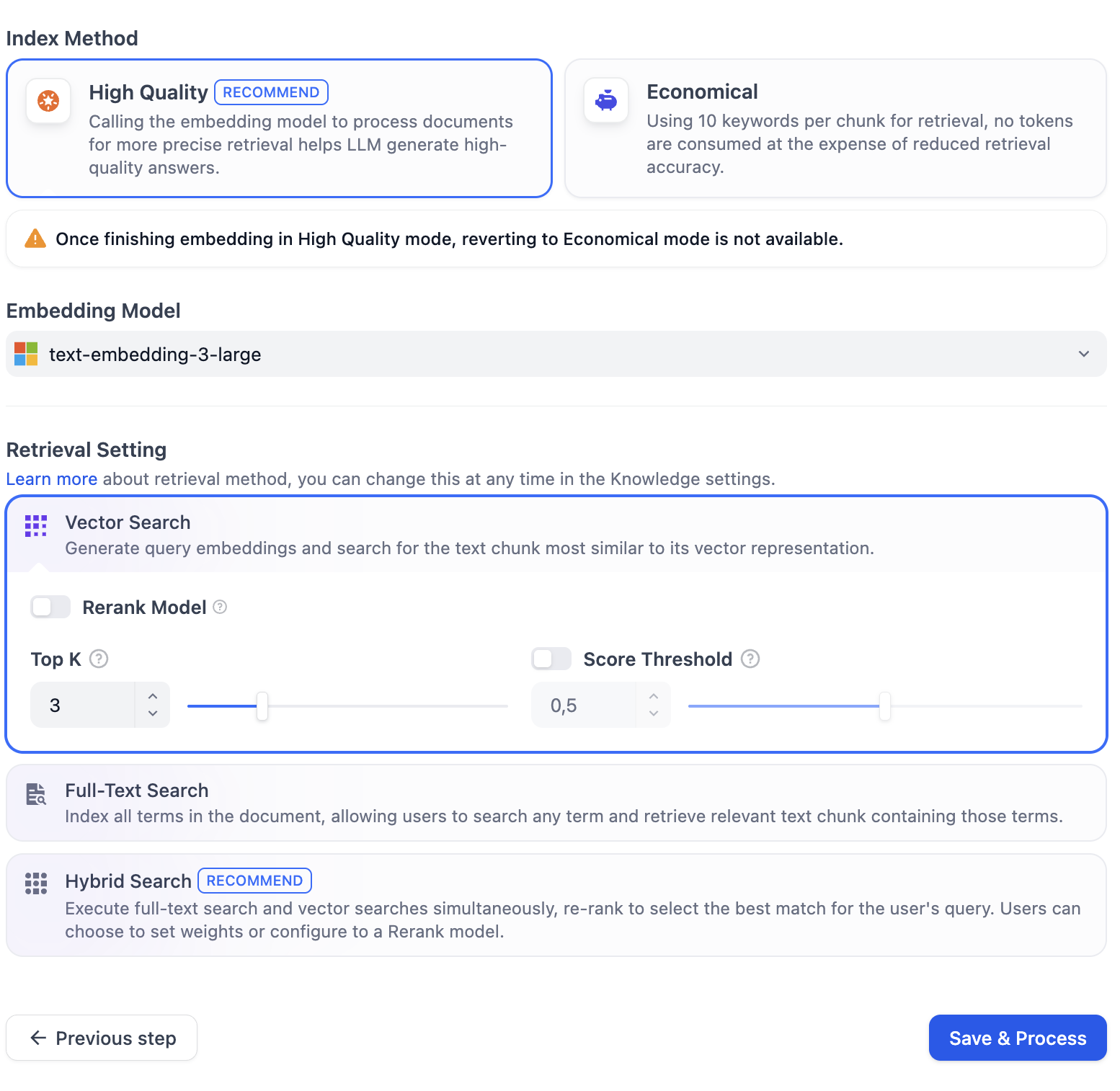
Click on Save & Process. You can now investigate your document chunks, sizes, content, etc. What do you think?
📦 Example Issue (JSON)
{
"summary": "Support 'expand' param on GET /rest/api/2/project",
"description": "The GET /rest/api/2/project endpoint should support 'expand' to allow additional project details.",
"issueType": "New Feature",
"priority": "Medium"
}
🧑💻 Advanced: Ingesting via API
Need a working config?
Why is API ingestion better?
- ✅ Supports more complex documents and formats.
- 🔁 Enables automation and batch processing.
- 📦 You can attach metadata (e.g.
issue_key) for filtering or analytics.